Abstract
Introduction: Mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) is an uncommon hematological malignancy with an estimated incidence of 1 per 100,000 persons per year in the United States and represents only about 5% of all non-Hodgkin lymphomas. Several studies have shown that treatment at academic centers and a higher hospital case volume are associated with improved outcomes for uncommon hematological malignancies, probably due to increased provider expertise and access to novel therapies. Treatment of MCL can be complex given the heterogenous nature of the disease and a frequent need for autologous stem cell transplantation in eligible patients. However, the impact of treatment at an academic center and facility patient volume on the survival of patients with MCL has not been well studied in large cohorts. In this study, we utilized the National Cancer Database (NCDB) to investigate the impact of treatment at an academic center and treatment facility volume on the overall survival (OS) of patients with MCL.
Methods: The NCDB was used to identify adult patients (≥ 18 years) with newly diagnosed MCL from 2004 through 2017. For facility patient volume analysis, patients were divided into groups based on the average number of new MCL patients seen annually: Tercile 1 [T1] (1-3 patients/year), Tercile 2 [T2] (4-5 patients/year) and Tercile 3 [T3] (≥6 patients/year). Treating centers were divided into Academic and Non-academic using the NCDB definitions. Academic centers were defined as centers that accessions more than 500 newly diagnosed cancer cases per year, participate in postgraduate medical education in at least four program areas including internal medicine and surgery and participates in cancer-related clinical trials. The primary endpoint was overall survival (OS). Survival analysis was performed using the Kaplan-Meier method and Cox hazards proportional model. Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS version 25.
Results: We identified 22,752 patients with MCL during the study period. 9,484 (42%) patients were treated at academic centers and 13,070 (57%) were treated at non-academic centers. In terms of facility patient volume 10,948 patients (48%) were in the T1 group, 4,637 (20%) were in the T2 group and 7,166 (31%) were in the T3 group. No significant differences were found in baseline demographics (age, gender, race/ethnicity, comorbidity scores), socioeconomical variables (insurance type, median income, area of residence) and disease-related factors (B-symptoms, Ann Arbor stage) between patients treated academic vs nonacademic centers, or between patients in T1 vs T2 vs T3 groups. Notably, compared to lower volume facilities, T3 facilities were more likely to be academic centers (T3: 81% vs T2: 42% vs T1: 16%, p<0.001) .
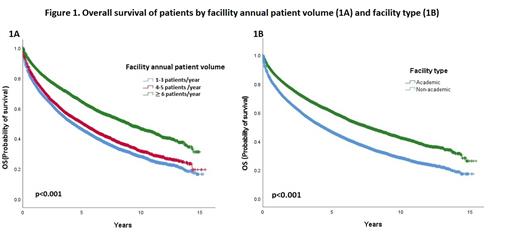
After a median follow-up of 3.4 years, the median overall survival (OS) was 5.6 years for the entire cohort. The median OS was inferior for patients treated at lower volume facilities (4.1 years for T1, 5.1 years for T2 and 9.0 years for T3, p<0.001) (Figure 1A). Similarly, the median OS was shorter for patients treated at non-academic centers vs academic centers (4.3 years vs 7.5 years respectively, p<0.001) (Figure 1B). In a multivariate analysis, treatment at a lower patient volume facility (Hazard ratio [HR] Q1= 1.26 [95%CI = 1.18-1.34]) and treatment at a non-academic center (HR = 1.1, 95%CI = 1.01-1.12) were both independent prognostic factors of inferior OS, after adjusting for demographics (age, gender, ethnicity, area of residence) and socioeconomic variables (income and insurance status).
Conclusion: Patients with MCL treated at academic and higher volume facilities had a higher OS compared to patients treated at non-academic and lower volume facilities.. Additional research is needed to fully understand the mechanisms behind these differences. Patients with MCL may benefit from an early referral to academic and high-volume centers.
Munoz: Merck: Research Funding; Portola: Research Funding; Genentech: Research Funding; Incyte: Research Funding; Janssen: Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics/Abbvie, Bayer, Gilead/Kite Pharma, Pfizer, Janssen, Juno/Celgene, BMS, Kyowa, Alexion, Beigene, Fosunkite, Innovent, Seattle Genetics, Debiopharm, Karyopharm, Genmab, ADC Therapeutics, Epizyme, Beigene, Servier: Consultancy; Gilead/Kite Pharma, Kyowa, Bayer, Pharmacyclics/Janssen, Seattle Genetics, Acrotech/Aurobindo, Beigene, Verastem, AstraZeneca, Celgene/BMS, Genentech/Roche.: Speakers Bureau; Millennium: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Research Funding; Celgene: Research Funding; Physicians' Education Resource: Honoraria; Gilead/Kite Pharma: Research Funding; Kyowa: Honoraria; Bayer: Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Honoraria; OncView: Honoraria; Targeted Oncology: Honoraria. Paludo: Karyopharm: Research Funding. Habermann: Seagen: Other: Data Monitoring Committee; Incyte: Other: Scientific Advisory Board; Tess Therapeutics: Other: Data Monitoring Committee; Morphosys: Other: Scientific Advisory Board; Loxo Oncology: Other: Scientific Advisory Board; Eli Lilly & Co.,: Other: Scientific Advisor. Nowakowski: Daiichi Sankyo: Consultancy; Zai Labolatory: Consultancy; TG Therapeutics: Consultancy; Blueprint Medicines: Consultancy; Nanostrings: Research Funding; MorphoSys: Consultancy; Kymera Therapeutics: Consultancy; Incyte: Consultancy; Ryvu Therapeutics: Consultancy; Kyte Pharma: Consultancy; Genentech: Consultancy, Research Funding; Roche: Consultancy, Research Funding; Celgene/Bristol Myers Squibb: Consultancy, Research Funding; Selvita: Consultancy; Curis: Consultancy; Karyopharm Therapeutics: Consultancy; Bantham Pharmaceutical: Consultancy. Wang: Novartis: Research Funding; LOXO Oncology: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; TG Therapeutics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Genentech: Research Funding; Eli Lilly: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; MorphoSys: Research Funding; InnoCare: Research Funding; Incyte: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal